The Internet is Getting a Makeover...It's Called Web 3.0
Web 3.0 is thought of as the dawn of the new Internet. But what do blockchain and cryptocurrency have to do with it? Read on for answers to these questions and more.

The Internet has been around for a few decades now and has had its share of ups and downs. From dial-up internet to massive data breaches to the explosion of social media, the Internet has been through a lot. We are in an era where augmented reality, metaverse, and blockchain are normal topics of conversation and technology has evolved to the point where, quite frankly, it requires a more sophisticated Internet to keep up. But there are some major housekeeping items to tackle first.
Big Tech is pickpocketing our data
One area of concern that Web 3.0 hopes to address is the overconcentration of data being hoarded by a handful of actors. Through our search queries, interactions on social media, and online shopping, the Internet has our digital footprints all over it. Unfortunately, this has resulted in companies collecting our information often without our acknowledgment or consent.
We are not blind to the fact that corporations use, manipulate and commercialize our data, and that we have little control over data ownership. Unfortunately, there is seemingly little reward for relinquishing our personal data, and there is not much we can do about it. This Pew Research study shows that 72% of adults say they feel very little benefit, if any, from company data collection about them.
Web 3.0 is created to support the needs of an increasingly digital world, while addressing the massive problem of data being controlled by corporations.
A brief history of the Internet
To understand the problems that Web 3.0 needs to solve, it helps to look at how the Internet has evolved over the years. Even with a relatively short history, it has seen some significant improvements in the past few decades.
In the early 1990s, the Internet was a landscape of hundreds of government and research organizations. As the personal computer began showing up in American households in the mid-1990s, there was more user-focused, and sometimes entertaining content like dating sites, Netflix, and the Google search engine. The early 2000s were defined by the introduction of social media sites like Facebook, YouTube and Twitter.
The 2010s was when we found out from Mr. Snowden that things weren't so good on the privacy front. And in this modern era of the Internet where the likes of Google and Amazon hold the bulk of our data in their giant corporate hands, we now realize that the free, open web we've come to know and love has a price.

Advocates for Web 3.0 have argued that Web 2.0 has drifted away from its participatory roots to a more centralized, corporate-controlled marketplace, where every engagement is tracked and every email monetized. Perhaps this is in large thanks to the FAANG companies (Facebook, Apple, Amazon, Netflix and Google), who are apt to use algorithms that are hidden from the public eye to manage content and influence what the user sees.
What is Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 (also known as Web3) is essentially the latest version of the Internet where users (as opposed to Big Tech) have more ownership over the data they use and share on the internet. The term decentralization is often used when talking about Web 3.0 as it refers to decentralizing the power of large organizations and allowing users to maintain control over their data.
One way to decentralize the Internet is through the use of blockchain technology, which is essentially a distributed, digital ledger that is used to record transactions of various types across the network. Blockchain technology will once again allow for a more participatory Internet where creators can exchange information and share value and where users own their data.
Dr. Gavin Wood, Web3 Foundation Founder and President and coiner of the term ‘Web 3.0’, provides the following definition of Web 3.0 during the M-0 conference in Zug, Switzerland: "Web3 is an extensible framework for creating massively multi-user, economically strong applications." 3
"Technology is facilitating a greater concentration of power." - Dr. Gavin Wood, Web3 Founder
Dr. Wood's vision of the Internet is as a "secure social operating system”, and he feels strongly about the misuse of power by the few, which affects the many. He also recognizes the need for a "zero-trust interaction system” as we move into the future.
Using B.E.A.D.S. to Explain Web 3.0
The Basic Principles of Web 3.0
- Blockchain will enable fair and efficient interactions by allowing users to hold their data in the blockchain and to send funds with cryptocurrencies.
- Edge computing is a new generation of digital technology where data is processed closer to where it is generated (aka the “edge” of the network). Edge computing will play a significant role in Web 3.0 because it enables the support of devices that rely on data at the source, such as augmented reality, smart cameras, and other IoT (Internet of Things) devices.
- Artificial Intelligence can leverage edge computing and blockchain technologies to train models to improve services and deliver more realistic and seamless experiences.
- Decentralized data exchange and sharing means that users will have more control over their data, breaking the monopoly that Big Tech companies have on data and data storage.
- Secure Global, Digital Transactions will mean using blockchain technology to help validate transactions and trace ownership. According to MIT, what makes the blockchain system more difficult to hack is the cryptographic fingerprint unique to each block, and a “consensus protocol", the process by which the nodes in the network agree on a shared history.6
Challenges Ahead for Web 3.0
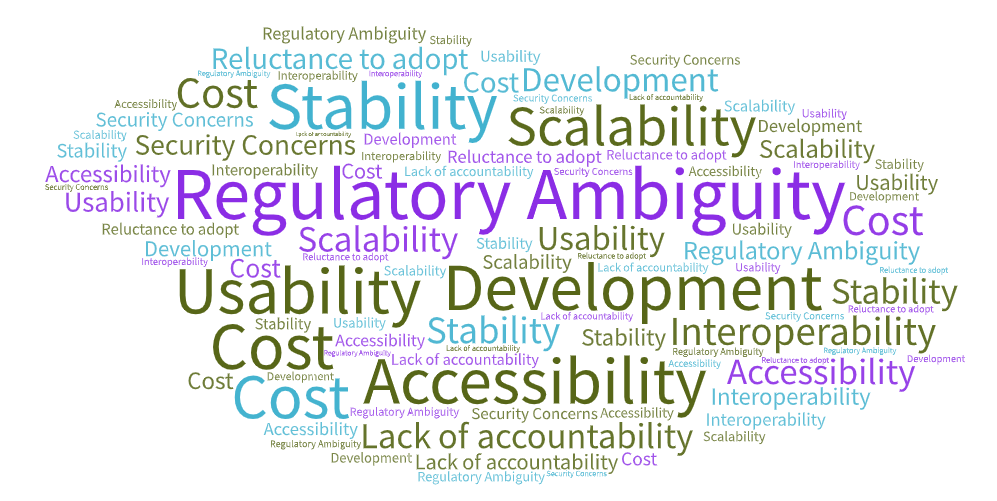
Web 3.0 will have to overcome the complexities that come with any major technological innovation, and there is no guarantee of a seamless transition. Users will find a higher learning curve to keep their activities secure in Web 3.0, and will likely have to continue using Web 2.0 to continue to receive the full benefits and functionality of the web. In addition, outdated technologies will not have much of a place in Web 3.0, which will put developing countries at a disadvantage. With these obstacles in mind, it will be a while before everyone can officially adopt the latest version of the web, but it is coming one way or another.
Conclusion
Web 3.0 will allow users to have more control over their data through decentralization. It will create a more secure Internet that supports the latest technologies like virtual reality, artificial intelligence, edge computing, and blockchain. As with any new technological innovation, it will have its share of challenges too, such as a new set of security issues (those will never go away), developmental complexity, and a steeper learning curve. Therefore, it is likely that Web 2.0 will continue to provide the majority of Internet functionality we need (for now) as Web 3.0 continues to develop and overcome its unique challenges.
Sources and Further Reading
- Abrol, A. (2023, February 15). Web 3.0 vs. Metaverse: A detailed comparison. Blockchain Council. https://www.blockchain-council.org/metaverse/web-3-0-vs-metaverse/
- ĐApps: What Web 3.0 Looks Like. (n.d.-b). https://gavwood.com/dappsweb3.html
- Enzyme. (2017, November 29). Dr. Gavin Wood - The Journey to Web3 [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lH1pEE0W3ug
- Less-techy: What is Web 3.0? (n.d.). https://gavwood.com/web3lt.html
- Lin, Y., Gao, Z., Tu, Y., Du, H., Niyato, D., Kang, J., & Yang, H. (2022). A Blockchain-based Semantic Exchange Framework for Web 3.0 toward Participatory Economy. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2211.16662.pdf
- Orcutt, M. (2020, April 2). How secure is blockchain really? MIT Technology Review. https://www.technologyreview.com/2018/04/25/143246/how-secure-is-blockchain-really/
- Pentland, A. (2022). Building a New Economy: Data, AI, and Web3: How distributed technologies could return more control to users. Communications of the ACM, 65(12), 27–29. Retrieved from Shapiro Library, Southern New Hampshire University, DOI: 10.1145/3547659.
- Web3 Foundation. https://web3.foundation/about/
- Wood, G. (2022, January 4). What Is Web 3? Here’s How Future Polkadot Founder Gavin Wood Explained It in 2014. https://www.coindesk.com/layer2/2022/01/04/what-is-web-3-heres-how-future-polkadot-founder-gavin-wood-explained-it-in-2014/
